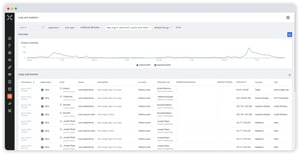
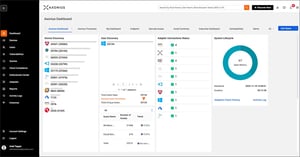
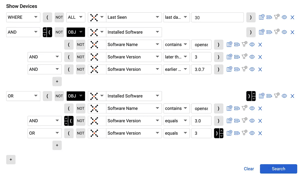
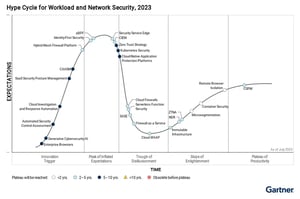
Cyber Asset Attack Surface Management (CAASM)
CVE-2024-3400: Active Exploitation of Critical Vulnerability in Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS Software
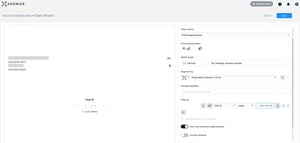
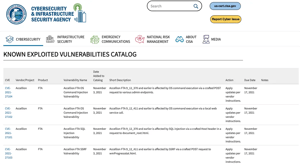
On April 12, 2024, Palo Alto Networks issued a security advisory regarding a critical vulnerability...

































































![Emerging Tech CAASM Isn’t Just the Hype [Cycle]](https://www.axonius.com/hs-fs/hubfs/2024%20Webp%20Blog%20Featured%20Images/BlogImage_Fed3_Orange_1200x628.webp?length=300&name=BlogImage_Fed3_Orange_1200x628.webp)